Services
Periodontal
LANAP Protocol
A Non-Invasive Breakthrough Procedure for Periodontal Patient Care
Less Pain, Less Bleeding, Less Recovery Time. The patented LANAP protocol is a minimally-invasive surgical method of treating and often reversing gum disease.
The LANAP protocol is the only laser periodontis treatment protocol that is cleared by the U.S. FDA for True Regeneration® and is clinically and histologically proven to regenerate new gum tissue, ligament, and bone.
Research has shown the PerioLase MVP-7 Nd:YAG wavelength stimulates the release of growth factors, allowing the body to heal naturally.
The LANAP protocol can also help loose dental implants. Using the PerioLase MVP-7, we can often save ailing or failing implants using the LAPIP protocol. We use the same laser, but different laser settings and light exposure to help implants stabilize while destroying periodontal pathogens and endotoxins.
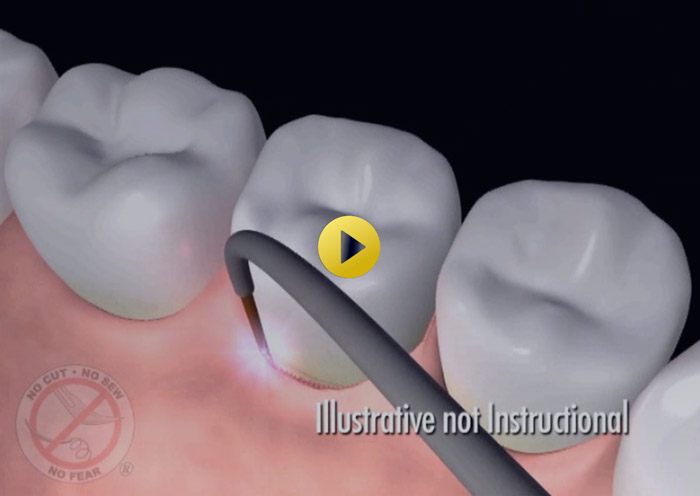
During the procedure, the PerioLase MVP-7 dental laser is used to gently remove harmful germs and diseased tissue from the gum pocket, keeping healthy tissue intact.
Overview of the LANAP Protocol
The image below illustrates the LANAP protocol steps:
- A. Periodontal probe indicates excessive pocket depth
- B. Laser light removes germs and diseased tissue
- C. Ultrasonic scaler removes root surface tartar
- D. Bone modification promotes new tissue growth
- E. Laser finishes cleaning pocket, stimulates growth factors, and aids in sealing the pocket closed
- F. Healing of gums to clean root surface occurs
- G. Bite trauma is adjusted
- H. Tissues and bone re-grow and healing occurs
The LANAP protocol is the only laser periodontis treatment protocol that is cleared by the U.S. FDA for True Regeneration® and is clinically and histologically proven to regenerate new gum tissue, ligament, and bone. Research has shown the PerioLase MVP-7 Nd:YAG wavelength stimulates the release of growth factors, allowing the body to heal naturally.
The LANAP protocol can also help loose dental implants. Using the PerioLase MVP-7, we can often save ailing or failing implants using the LAPIP protocol. We use the same laser, but different laser settings and light exposure to help implants stabilize while destroying periodontal pathogens and endotoxins.
LANAP Protocol featured on ABC News Now - Healthy Life
"A New Gum Disease Procedure”Dr. Robert H. Gregg, developer of Laser Periodontal Therapy, discusses how scalpel-free dental laser therapy successfully treats the cause of gum disease (bacteria and resulting endotoxins) with less pain, less bleeding, less infection, and less recovery time. Airdate: May 6, 2008

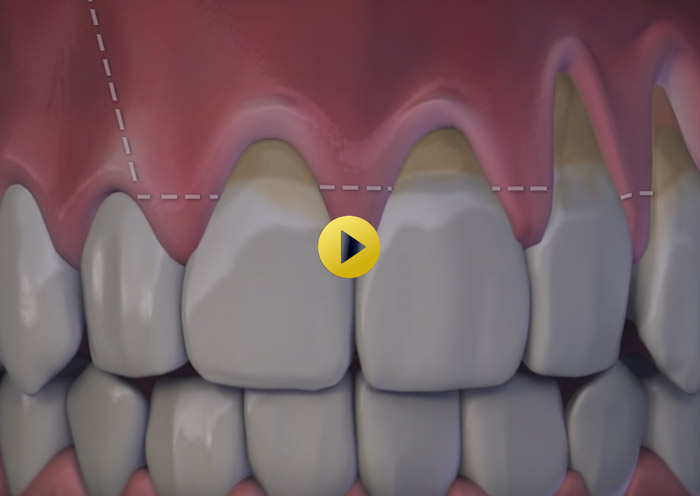
Receding Gums - Pinhole Surgical Technique
What are the consequences of gum recession?
Gum recession is the process in which the margin of the gum tissue that protects the teeth wears away, or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth root. When gum recession occurs, “pockets”, or gaps form between the teeth and gumline, therefore, making it easy for disease causing bacteria to build up an destroy teeth. If left untreated, the supporting tissue and bone structures of the teeth can be severely damaged and may ultimately result in tooth loss and even severe health consequences. Gum recession is a common dental problem and most people do not know that they have gum recession because it occurs gradually. The first sign of gum recession is usually tooth sensitivity or you may notice teeth that look longer than normal. Typically, a notch can be felt near the gum line. Do not ignore gum recession! Early detection and treatment is essential to maintaining overall health and saving teeth. If you think that your gums are receding, make an appointment immediately for an evaluation of your individual case.
Why do gums recede?
Periodontal disease.
These are bacterial gum infections that destroy gum tissue and the supporting bone that holds teeth in place. Gum disease is the main cause of gum recession and loss of teeth. Due to genetics, some people may be more susceptible to gum disease. In fact, studies show that 30% of the population maybe pre-disposed to gum disease, regardless of how well they care for their teeth.
Insufficient dental care.
Inadequate brushing and flossing make it easy for plaque to turn into calculus (tartar) – a hard substance that builds on and between teeth. This type of plaque can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
Hormonal changes.
Fluctuations in female hormone levels during a woman’s lifetime, such as in puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and more vulnerable to gum recession.
Grinding and clenching teeth
Clenching or grinding teeth can put too much force on the teeth, causing gums to recede. Clenching during sleep is a common cause of gum recession.
Tobacco products
Tobacco users are more likely to have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove and can cause gum recession.
Crooked teeth or a misaligned bite
When teeth do not come together evenly, excessive force can be placed on the gums and bone, allowing gums to recede.
Body piercing of the lip or tongue
Jewelry can rub the gums and cause irritation to the point that gum tissue is worn away.
Aggressive tooth brushing.
Brushing teeth and gums too hard can cause gum recession.
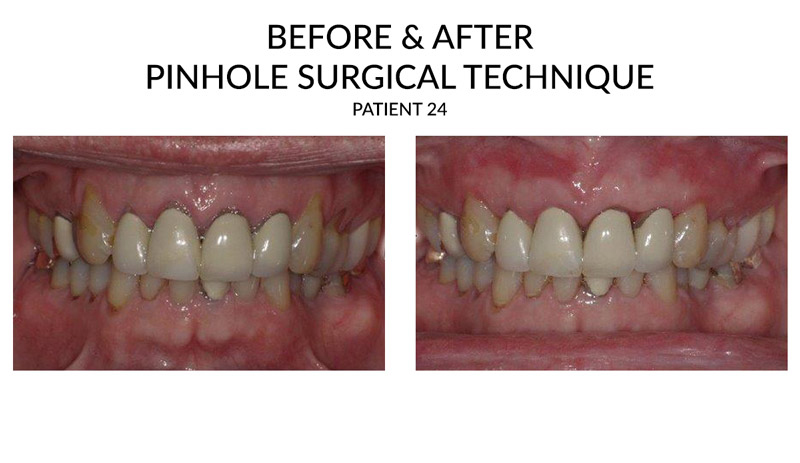
Pinhole® Surgical Technique for Receding Gums
A Scalpel-Free, Suture-Free, Minimally Invasive Procedure
The Chao Pinhole® Surgical Technique, also known as Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation, was invented and patented by John Chao, D.D.S. It is a scalpel-free, suture-free, graft-free, minimally invasive procedure for correcting gum recession and saving teeth. Through a small hole made by a needle, specially designed instruments are used to gently loosen the gum tissue and glide it over the receded part of the tooth. Since there is no cutting or stitching, patients can expect minimal post-operative symptoms (pain, swelling and bleeding). Patients are pleasantly surprised by the instant cosmetic improvement. Most patients are able to resume light normal activities within 24-48 hours after treatment.
Benefits of the Pinhole® procedure
- Can correct gum recession in as little as 1 treatment session.
- Minimal discomfort and swelling in most cases because the method is scalpel-free, suture-free and graft-free.
- Long-term results per the International Journal of Periodontology & Restorative Dentistry. (October2012)
- The pinholes heal in 24 hours in most cases.
- Only 2 over-the-counter pain pills required after treatment on average per the study in the Int. Journal of Periodontology & Restorative Dentistry. (October2012)
- Can prevent tooth loss and the need for other costly procedures such as implants or dentures.
- Treatment sessions can be completed in as little as 1-2 hours in many cases.
- Can enhance a more youthful and attractive appearance.
- Patients often describe feeling happier due to being able to smile without the shame or guilt associated with receded gums.
- Most patients are back to normal light activities within 24-48 hours post-procedure.
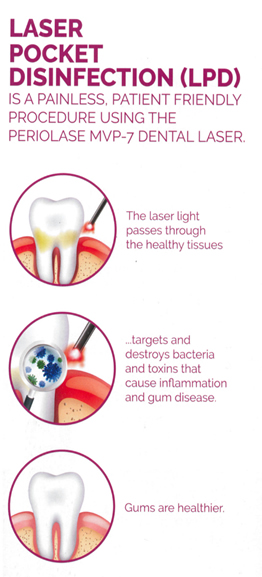
Laser Pocket Disinfection
(LPD)
A Painless Procedure Using the PerioLase MVP-7 Dental Laser - The PerioLase MPV-7 is the only dental laser specifically designed for better periodontal health. The unique wavelength targets the bacteria that causes gum disease for minimally invasive, highly effective, quick and painless treatment.
How Are Porcelain Veneers Done?
- Kills bacteria and disrupts biofilm to reduce inflammation
- Can help reverse gingivitis symptoms
- Maintain healthy gums and avoid progression of gum disease
- No shots needed
- No antibiotics needed, avoids antibiotic resistance
- No known side-effects of LPD in over 25 years of therapy
- The Iaser light can reach and destroy bacteria up to 6mm beyond the surface to help prevent bacteria from spreading back into the pocket.
- Safe for medically compromised patients, those on blood thinners, or those with diabetes
- Safe for use around crowns, bridges, sealants, and implants
- Beneficial to patients who have recently had surgery, or are scheduled to have surgery to reduce bacteria that may enter the bloodstream
Gum Disease & Your Health
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease begins when a film called plaque accumulates on the teeth and calcium from saliva hardens the plaque—this calcified plaque is called tartar or calculus. Certain types of germs that live in this plaque and calculus damage gum tissue. Your body tries to fight this infection with an inflammatory attack, sending white blood cells to the area to destroy the bacteria. This inflammation causes the tissue to bleed easily when you brush or floss. This stage of the condition is called gingivitis. If the infection and inflammation persist, the result is a chronic inflammatory condition where the gums, ligament and bone around the teeth are destroyed—often with no symptoms. This stage is called periodontitis.
Signs/Symptoms of Moderate—Advanced Gum Disease Include:
- Gums that are red, swollen, and bleed easily
- Gums that seem to have pulled away from the teeth
- Bad breath or halitosis
- Pus between your teeth and gums
- Teeth that seem to be loose or moving away from one another
- Change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Change in the way your partial denture or implant-supported restorations fit
- Or no symptoms at all!
What Is Gum Disease?
- Well known risk factors for periodontitis include genetics, stress, avoiding the dentist, not brushing or flossing, and some medical conditions. Smokers are significantly more likely to develop gum disease than non-smokers.
- It’s not just about your teeth anymore — gum disease has been linked to numerous health problems, with new studies emerging all the time linking oral and overall health.
The Link Between Gum Disease, Heart Disease, and Stroke
- Research indicates gum disease may increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. People with gum disease are twice as likely to have heart disease. Those diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke (brain injury caused by a blocked blood vessel) are more likely to have gum disease.
- The presence of common problems in the mouth, including gum disease, cavities, and missing teeth, were as good at predicting heart disease as cholesterol levels.
The Possible Connection: Oral Bacteria
- Bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream through the gums.
- Oral bacteria stick to fatty plaques in the bloodstream, directly contributing to blockages.
- Oral bacteria trigger and inflammatory response, causing the blood vessels to swell, reducing blood flow, and increasing the risk of clots.
Proactive Prevention: Oral Health Affects Total Health
- Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings
- Brushing regularly
- Flossing regularly
- If you have gum disease plus one risk factor of heart disease, have an annual medical exam to check your heart health.
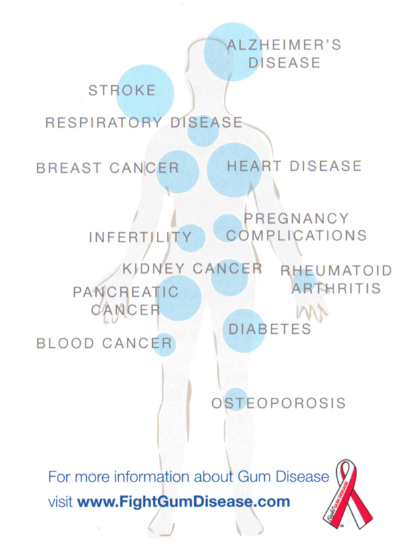
Gum Disease and Your Whole Body Health
Over 50% of adults in the U.S. have some degree of gum disease, but did you know the impact goes far beyond your mouth?
- Osteoporosis – People with gum disease may be at a higher risk of osteoporosis.
- Stroke – People with severe gum disease have a 3x to 4x higher risk of brain stroke.
- Alzheimer’s and Dementia – Gum disease may be linked to Alzheimer’s disease and dementia from oral bacteria that spread through the bloodstream.
- Cancer – Several studies show strong evidence linking gum disease with an increased risk of oral cancer and pancreatic cancer.
- Respiratory Disease – Gum disease can worsen conditions such as COPD and may play a role in the contraction of pneumonia, bronchitis, and emphysema.
- Heart Disease – People with gum disease are 2x as likely to have heart disease.
- Diabetes – Nearly 22% of diabetes patients have gum disease.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – RA patients are 8x more likely to have gum disease.
Statistically, gum disease is higher in men (56.4%) than in women (38.4%).
- Impotence – Men in their 30s with severe gum disease are 3x more likely to suffer from erectile dysfunction. Prolonged chronic inflammation associated with gum disease can damage blood vessels leading to impotence.
- Prostate Health – Studies show that the prostate-specific antigen (PSA), an enzyme created in the prostate that is normally secreted in very small amounts, is secreted at higher levels in men with gum disease and prostate cancer.
- Cancer in Men – Research has found that men with a history of gum disease are 14% more likely to develop cancer than men with healthy gums. Men with gum disease may be 49% more likely than women to develop kidney cancer, 54% more likely to develop pancreatic cancer, and 30% more likely to develop blood cancers.
- Puberty and Menstruation – An increased level of sex hormones causes higher blood circulation to the bums, increasing the gum’s sensitivity, susceptibility to irritation, and the growth of bacteria just beneath the gums. These same hormones can cause menstruation gingivitis – red, swollen, tender or bleeding gums, and sores on the inside of the cheek, which typically occurs right before a woman’s period and clears up once it has started.
- Pregnancy and Preterm Births – Pregnant women with untreated gum disease may be more likely to have a preterm baby.
- Menopause and Post-Menopause – Women may experience changes in their mouths, including discomfort in the mouth, dry mouth, pain and burning sensations in the gum tissue, and altered taste. In addition, post-menopausal women with osteoporosis are 86% more likely to develop gum disease, while women with gum disease have a higher risk of having osteoporosis.
Gum Therapy
The health of your mouth, teeth, and gums has a direct impact on your overall health. This relationship has recently been coined as Oral Systemic Connection. Research has recently found that the same bacteria that causes gums to become inflamed can travel throughout the body, including to cells in the coronary arteries. Recent reports have linked gum disease with Heart Disease, Stroke, Diabetes, Pregnancy problems, Increased risk of pancreatic cancer.
Traditional gum surgery is the removal of the periodontal disease-causing bacteria that lives below the gumline.
How Is Traditional Gum Surgery Done?
Traditional gum surgery procedure is also referred to as flap surgery, or pocket reduction surgery, during which the gum is gently lifted back to remove the tartar that has accumulated below the gumline. The gums are then reattached to the newly sterilized surface to heal.
Am I a Candidate for Traditional Gum Surgery?
Candidates for Traditional Gum Surgery are those with red, swollen, bleeding or tender gums, chronic bad breath, and those with periodontal disease.
After Treatment
Recovery time and post-surgery needs differ from person to person. During this time, it is important to follow the instructions and medications given to you. Be sure to keep all areas in your mouth clean after surgery, use ice packs to minimize swelling, and avoid very hot liquids initially after surgery.
5 Treatment Choices
Periodontal disease is an ongoing, slowly progressing disease.
Unless it is treated, it will continue to destroy your dentition. Research shows that periodontal disease is related to causing heart disease, strong, and diabetes.
The following information describes the various treatments for periodontal disease, from least to most aggressive.
- No Treatment. If you elect to do nothing to treat your periodontal disease, it will continue to progress slowly until you lose the involved teeth. Tooth loss can require a few months to years. Routine dental hygiene appointment can increase the possibility of increase tooth longevity, but more comprehensive treatment is usually indicated.
- Increased frequency of typical oral hygiene appointments and use of additional conservative treatments. Although normally tooth cleanings or scalings are performed once ever 6 months, patients with minimal periodontal disease can often control its progress by increasing the frequency of scalings and exams to once every two or three months, often accompanied by medication, tongue cleaning, rinses, and other treatments.
- Deep scaling, root planning, and soft tissue curettage (removal of inflamed tissue) and increase frequency of oral hygiene appointments.Removal of tartar from the deepest areas of the periodontal pockets, planing of the tooth root surfaces and removal of the diseased soft tissue by curettage, usually decreases pocket depts and slows the progress of periodontal disease. Scaling, polishing, and examination are increased to once every tow or three months. Systemic and local antibiotics, tongue cleaning, rinses, and other treatments including laser therapy may be included in this treatment.
- Periodontal surgery. In advanced cases it may be necessary to gently reflect the gums from the underlying bone tissue, clean out the infection, sometimes add bone grafts in deficient areas, and replace the gums to allow healing This surgical treatment is followed by frequent cleaning/scaling appointments
In addition to the above treatments, patients should improve their oral hygiene procedures and diet. Smoking is an extremely negative factor related to periodontal disease, and it should be reduced or, preferably, stopped.
Periodontal Disease Treatment: Surgery or a Conservative Approach?
- If you have periodontal disease, the condition will slowly progress, eventually weakening bone support of the teeth, causing the need for tooth extraction. There are two options for treatment of this condition:
- Surgical, in which the diseased gum and bone tissue are removed and/or reshaped to allow proper cleaning.
- Conservative, explained below, in which you must have an active role in carrying out the procedures described below
- The following are procedures included in conservative periodontal therapy:
- We will provide information for you to better understand the disease.
- We will provide hygiene instruction to allow you to upgrade your oral cleaning habits.
- We will demonstrate tongue cleaning to you. The tongue is a reservoir for billions of microorganisms that cause periodontal disease.
- Daily antimicrobiologic rinses will be suggested from the first appointment of your conservative therapy.
- Professional scaling, root planning, and polishing of the teeth will be provided for you every two or three months. This may be augmented with laser treatments.
- Low level systemic antibiotic therapy to control the organisms causing periodontal disease will be prescribed for you if periodontal disease is still active in your mouth after two or three months of the previous treatments.
- Local antibiotics will be delivered to the most affected areas of your mouth if you do not respond positively after two or three months of previous treatments.
- Both surgical and conservative therapy can be successful in treating periodontal disease. We will help you decide which is the best for you.
713.622.1707 | 713.622.5046
3355 West Alabama, Suite 200
Houston, TX 77098
info@maryrileydds.com

Mary F.Riley,D.D.S.,P.C.
Aesthetic Restorative Dentistry