Dental Wellness
Research indicates gum disease may increase the risk of heart disease and stroke; the presence of common problems in the mouth, including gum disease, cavities, and missing teeth, were as good at predicting heart disease as cholesterol levels. Oral bacteria is a possible connection since bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream through the gums, oral bacteria stick to fatty plaques in the bloodstream (directly contributing to blockages), and oral bacteria trigger an inflammatory response, causing the blood vessels to swell, reducing blood flow, and increasing the risk of clots.
Proactive prevention is the best defense.
Over 50% of adults in the U.S. have some degree of gum disease, but did you know the impact goes far beyond your mouth?
- Osteoporosis – People with gum disease may be at a higher risk of osteoporosis.
- Stroke – People with severe gum disease have a 3x to 4x higher risk of brain stroke.
- Alzheimer’s and Dementia – Gum disease may be linked to Alzheimer’s disease and dementia from oral bacteria that spread through the bloodstream.
- Cancer – Several studies show strong evidence linking gum disease with an increased risk of oral cancer and pancreatic cancer.
- Respiratory Disease – Gum disease can worsen conditions such as COPD and may play a role in the contraction of pneumonia, bronchitis, and emphysema.
- Heart Disease – People with gum disease are 2x as likely to have heart disease.
- Diabetes – Nearly 22% of diabetes patients have gum disease.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – RA patients are 8x more likely to have gum disease. Statistically, gum disease is higher in men (56.4%) than in women (38.4%).
- Impotence – Men in their 30s with severe gum disease are 3x more likely to suffer from erectile dysfunction. Prolonged chronic inflammation associated with gum disease can damage blood vessels leading to impotence.
- Prostate Health – Studies show that the prostate-specific antigen (PSA), an enzyme created in the prostate that is normally secreted in very small amounts, is secreted at higher levels in men with gum disease and prostate cancer.
- Cancer in Men – Research has found that men with a history of gum disease are 14% more likely to develop cancer than men with healthy gums. Men with gum disease may be 49% more likely than women to develop kidney cancer, 54% more likely to develop pancreatic cancer, and 30% more likely to develop blood cancers.
- Puberty and Menstruation – An increased level of sex hormones causes higher blood circulation to the bums, increasing the gum’s sensitivity, susceptibility to irritation, and the growth of bacteria just beneath the gums. These same hormones can cause menstruation gingivitis – red, swollen, tender or bleeding gums, and sores on the inside of the cheek, which typically occurs right before a woman’s period and clears up once it has started.
- Pregnancy and Preterm Births – Pregnant women with untreated gum disease may be more likely to have a preterm baby.
- Menopause and Post-Menopause – Women may experience changes in their mouths, including discomfort in the mouth, dry mouth, pain and burning sensations in the gum tissue, and altered taste. In addition, post-menopausal women with osteoporosis are 86% more likely to develop gum disease, while women with gum disease have a higher risk of having osteoporosis.
Why Is It Important To Get My Gum Disease Treated?
The health risks of gum disease go far beyond the loss of teeth. There is a connection between gum disease and a number of serious medical conditions.
- Are almost twice as likely to suffer from coronary artery disease
- Have nearly twice the risk of having a fatal heart attack.
- Respiratory disease
- Diabetes
- Alzheimer’s
- Certain cancers
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Osteoporosis
- Erectile dysfunction
- HPV
- Pregnancy complications
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease begins when a film called plaque accumulates on the teeth and calcium from saliva hardens the plaque—this calcified plaque is called tartar or calculus. Certain types of germs that live in this plaque and calculus damage gum tissue. Your body tries to fight this infection with an inflammatory attack, sending white blood cells to the area to destroy the bacteria. This inflammation causes the tissue to bleed easily when you brush or floss. This stage of the condition is called gingivitis. If the infection and inflammation persist, the result is a chronic inflammatory condition where the gums, ligament and bone around the teeth are destroyed—often with no symptoms. This stage is called periodontitis.
Signs/Symptoms of Moderate—Advanced Gum Disease Include:
- Gums that are red, swollen, and bleed easily
- Gums that seem to have pulled away from the teeth
- Bad breath or halitosis
- Pus between your teeth and gums
- Teeth that seem to be loose or moving away from one another
- Change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Change in the way your partial denture or implant-supported restorations fit
- Or no symptoms at all!
What Are the Risk Factors for Gum Disease?
Well known risk factors for periodontitis include genetics, stress, avoiding the dentist, not brushing or flossing, and some medical conditions. Smokers are significantly more likely to develop gum disease than non-smokers. It’s not just about your teeth anymore — gum disease has been linked to numerous health problems, with new studies emerging all the time linking oral and overall health.
The Link Between Gum Disease, Heart Disease, and Stroke
Research indicates gum disease may increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. People with gum disease are twice as likely to have heart disease. Those diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke (brain injury caused by a blocked blood vessel) are more likely to have gum disease. The presence of common problems in the mouth, including gum disease, cavities, and missing teeth, were as good at predicting heart disease as cholesterol levels.
The Possible Connection: Oral Bacteria
- Bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream through the gums.
- Oral bacteria stick to fatty plaques in the bloodstream, directly contributing to blockages.
- Oral bacteria trigger and inflammatory response, causing the blood vessels to swell, reducing blood flow, and increasing the risk of clots.
Proactive Prevention: Oral Health Affects Total Health
- Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings
- Brushing regularly
- Flossing regularly
If you have gum disease plus one risk factor of heart disease, have an annual medical exam to check your heart health.
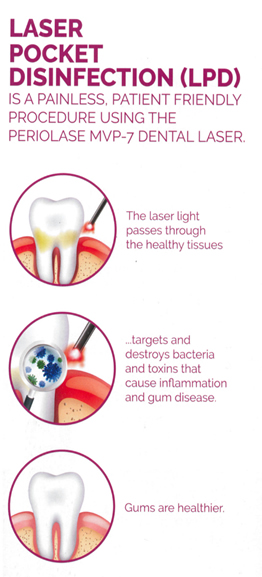
Laser Pocket Disinfection (LPD)
LPD kills bacteria and disrupts biofilm to reduce inflammation. When isolated pocketing is present, LPD decreases pocket depths without curettage. Ideal for patients with gingivitis.Benefits:
- Quick and painless procedure to help maintain healthy gums and avoid progression of the disease
- Removes the inflammation so your body can heal naturally without antibiotics
- Safe for medically comprised patients, patients on blood thinners, and diabetic patients
Biostimulation - Pain Reduction from TMJ and Orthodontics
Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) or biostimulation can be used for many applications within dentistry, in particular to reduce the pain associated with orthodontics or temporomandibular disorder (TMJ).Benefits:
- Relieves pain associated with TMJ
- Stimulates the body’s own healing process by increasing blood flow to the affected area
- Helps relax muscles and block inflammation
Canker Sores - Aphthous Ulcers
Aphthous ulcers are painful, yet generally disappear without treatment in 10-14 days. Ulcers aren’t infectious and tend to recur less with age. The cause is not known, but related factors include injury, changes in hormone levels, lack of iron, food allergies, stress, and certain medications.Benefits:
- Eliminates pain associated with the aphthous ulcer
- Increases patient convenience by avoiding having to reschedule appointment because of pain from site
- For particular large ulcers, treatment can speed the healing process
Cold Sores - Herpetic Lesion (Viral Therapy)
Herpetic lesions can occur in three different forms: recurrent small blisters on the lips, a generalized oral infection, or small ulcers on the palatal mucosa. The most common form is small blisters on the lips, which can be treated with low level laser therapy. Outbreaks may be triggered by sunlight, physical trauma, stress, and other irritants. Lesions will usually resolve in 10-14 days, but may be painful.Benefits:
- Safe, quick, and comfortable treatment that relieves pain
- Immediate relief
- Lesions can be treated before a breakout if patients feel an “onset”
- Laser treatments can help reduce the number of cold sores and severity of future outbreaks
- For particular large ulcers, treatment can speed the healing process
- No anesthesia needed
Desensitization
Dental sensitivity affects more than 40% of adults worldwide, and more than 40 million people in the United States. [1] Exposed dental tubules are believed to be the predominate cause, with sensitivity to heat and cold the most common complaint. Laser therapy can help close tubules and reduces sensitivity.
[1] Prevalence of dentine hypersensitivity in a general dental population. Irwin CR, P. Ir Dent Assoc. 1997; 43(1):7-9.
Benefits:
- Relieves discomfort of sensitive teeth
- Can be performed before or after restorative treatments to increase patient comfort
Tongue Cleaning
Most people brush their teeth routinely. The value of this simple procedure is well known and accepted. Tooth brushing removes dental plaque – the slimy substance that accumulates on tooth surfaces and causes tooth decay and periodontal (gum) disease. Plaque contains millions of bacteria, but did you know your tongue is the home for far more organisms than those that reside in the dental plaque on your teeth?
Here are some little-known facts:- The taste buds on the tongue vary in strength. Some people, about 50% of the population, have taste buds so long and dense that their tongues always have a gray, green, brown scum on them. The scum contains the same organisms that cause dental decay and gum disease.
- About 50% of the population (those with long taste buds) need to clean their tongues as a daily routine.
- It has been estimated that up to 90% of bad breath originates from organisms and debris on the surface of the tongue.
Decide if you need to clean your tongue. Stick it out. Is it pink? If so, cleaning is probably not necessary. Is it grey, orange, brown, or even black? You need to clean it. Brushing the tongue removes some of the organisms, but there is a better, easier, and more effective tongue cleaning procedure. Use the tongue cleaner we will suggest. Place it as far back on the tongue as you can tolerate. Place about one pound of force and pull the tongue cleaner forward. Repeat the procedure until no more debris is present. One or two cleanings per day is normal, especially before bedtime. You will be on your way to a cleaner mouth, less dental disease, and better breath.
Fluoride as Preventative Therapy
As a group, dentists and physicians, as well as global health organizations favor use of fluoride in all of the following methods. Fluoride for reduction of dental decay has had more legitimate worldwide research than any other health related subject. Nevertheless, there are some groups that oppose fluoride use for various political and alleged health reasons.
The decision to use fluoride for your and your family is up to you. For almost all dentists and physicians, “anti-fluoride” arguments make no sense at all.
- Use of small amounts of fluoride in community water supplies has been shown to significantly reduce dental decay. Your water supply may contain fluoride. If you do not know, ask your dentist, dental hygienist, or dental assistant.
- Where fluoride in water supplies is not available, addition of fluoride to the diet of children whose teeth are still developing has been shown to similarly reduce the development of dental decay. About one milligram per day is the optimal dosage, with lesser amounts for young children (we will advise you of the amount for your child).
- Application of rosin containing fluoride to teeth by your dentist or dental hygienist is well-known to significantly reduce the possibility for dental decay.
- Placement of fluoride on teeth in the form of rinses can reduce new dental decay, depending on the concentration of fluoride.
- Strong fluorides are used for patients who have high decay potential, such as those receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy, or those in orthodontic therapy.
Sealants
Why Seal Teeth?Over the past many years, numerous materials and techniques have been developed to seal the chewing (occlusal) surfaces of teeth. Sealants are necessary because some teeth have defective occlusal surfaces when they erupt into the mouth, and food debris and microorganisms penetrate into the grooves on the teeth during eating. Patients cannot clean these areas effectively, and dental decay (caries) occurs frequently.
Do All Teeth Need to Be Sealed?Usually only the back (posterior) teeth require sealing. It is difficult to tell which teeth require sealing because incomplete fusion of the teeth often leaves a microscopic entry from the enamel outside the tooth into the softer dentin inside. Therefore, we suggest that all suspect permanent posterior teeth and selected anterior teeth be sealed as closely to their eruption time as possible.
Will All Decay Be Prevented?Sealants placed as close to the eruption time of the teeth as possible prevent the majority of decay on the chewing (occlusal) surfaces of the teeth. However, flossing, brushing, and routine fluoride therapy are required to prevent decay on the other surfaces of the teeth. In the presence of poor oral hygiene, decay may begin between the teeth, since sealants cannot be placed on these surfaces.
CostThe cost for sealing a tooth with plastic is about one-fourth to one-third the cost of filling (restoring) the tooth in the event of decay. Sealants do not require anesthetic or cutting away tooth structure.
How Long Do Sealants Last?Studies show that properly placed sealants last many years. However, occasional resealing may be required.
Laser Pocket Disinfection (LPD)
A Painless Procedure Using the PerioLase MVP-7 Dental LaserThe PerioLase MPV-7 is the only dental laser specifically designed for better periodontal health. The unique wavelength targets the bacteria that causes gum disease for minimally invasive, highly effective, quick and painless treatment.
- Kills bacteria and disrupts biofilm to reduce inflammation
- Can help reverse gingivitis symptoms
- Maintain healthy gums and avoid progression of gum disease
- No shots needed
- No antibiotics needed, avoids antibiotic resistance
- No known side-effects of LPD in over 25 years of therapy
- The Iaser light can reach and destroy bacteria up to 6mm beyond the surface to help prevent bacteria from spreading back into the pocket.
- Safe for medically compromised patients, those on blood thinners, or those with diabetes
- Safe for use around crowns, bridges, sealants, and implants
- Beneficial to patients who have recently had surgery, or are scheduled to have surgery to reduce bacteria that may enter the bloodstream
Laser Cavity Detection - Diagnodent®
Diagnodent® scans teeth for hidden decay, often detecting cavities long before they can be seen by the naked eye. When we catch a cavity early, a smaller filling can usually be placed and preserve more of your natural tooth.
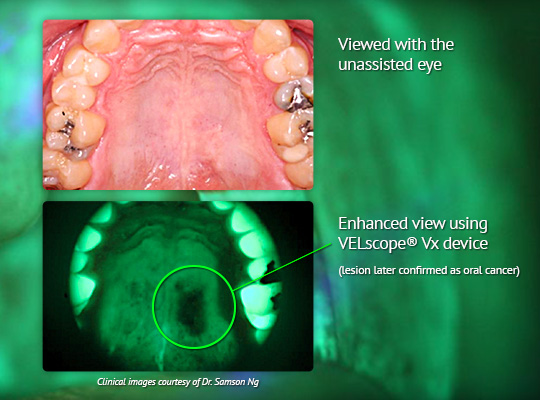
Oral Cancer Screening
A Two-Minute Exam Could Save Your LifeOral cancer is not something you hear about on a routine basis. Oral cancer has been related to smoking, chewing tobacco, irritation of oral soft tissue, various foods, alcohol and many other potential causes. However, contrary to popular knowledge, oral cancer has a slightly higher death rate than the more well-known cancer, melanoma. There are over 40,000 new cases of oral cancer each year in the U.S.
When oral cancer is treated, often the result is disfiguring to the face. Oral cancer is often fatal.
While there are several methods to determine if you may have oral cancer, our office uses the most cutting edge technology recognized by the World Health Organization for early detection of oral cancer, while it is still easy to treat. The VELscope Vx helps us identify oral disease early with blue light that stimulates natural fluorescence in the soft tissues of the mouth, showing disease not visible to the naked eye under ordinary light. One of the most important tasks of this VELscope Vx screening is to help locate areas that might, if not treated, progress to oral cancer.
Please ask us about oral cancer screening today.